Overview of Translations
The following is a high-level overview of the technologies associated with Translations.
Supported Platforms
Desktop
Android
iOS
Language Translation
Translations utilizes trained machine-learning models that run locally on client architecture to translate web content from one language to another.
Technology
Translations utilizes a WASM version of the Bergamot library to translate from one language to another. Bergamot is powered by Marian.
Models
Bergamot translation models are single-direction, one-to-one models trained to translate from one language
to one other language (e.g. en ⟶ es). When Translations determines a source language and a target language
it utilizes a model specific to this language pair to translate from one to the other.
Pivot Translations
In the event that there is no model to translate directly from a source language and a target language, Translations will attempt to satisfy a transitive translation path and will perform a multi-step translation from the source language to the target language.
Example
No direct translation model exists
es ⟶ frTransitive dependency satisfied
es ⟶ en
en ⟶ frPivot translation
es ⟶ en ⟶ fr
In this example, no direct model exists for es ⟶ fr, but a transitive dependency is satisfied by the two
models for es ⟶ en and en ⟶ fr. Translations will pivot on the en language by first
translating from es to en and then from en to fr.
Note
Translations will not pivot more than once.
At present, only
enis used as a pivot language.
Language Identification
Translations utilizes trained machine-learning models that run locally on client architecture to identify content as being written in a detected language.
Technology
Translations utilizes a CLD2 language detector to identify in which language content is written.
Models
No models are currently used for language identification, since CLD2 exists in the Firefox source tree.
Remote Settings
Remote Settings is not currently used for language identification, since CLD2 exists in the Firefox source tree.
Using Translations
The following documentation describes a high-level overview of using Translations.
Translating Web Pages
Firefox analyzes each web page to determine if it is translatable via the available translations models.
If the web page is translatable, then a translations icon will appear in the URL bar of the browser, allowing the user to initiate the available translation process.
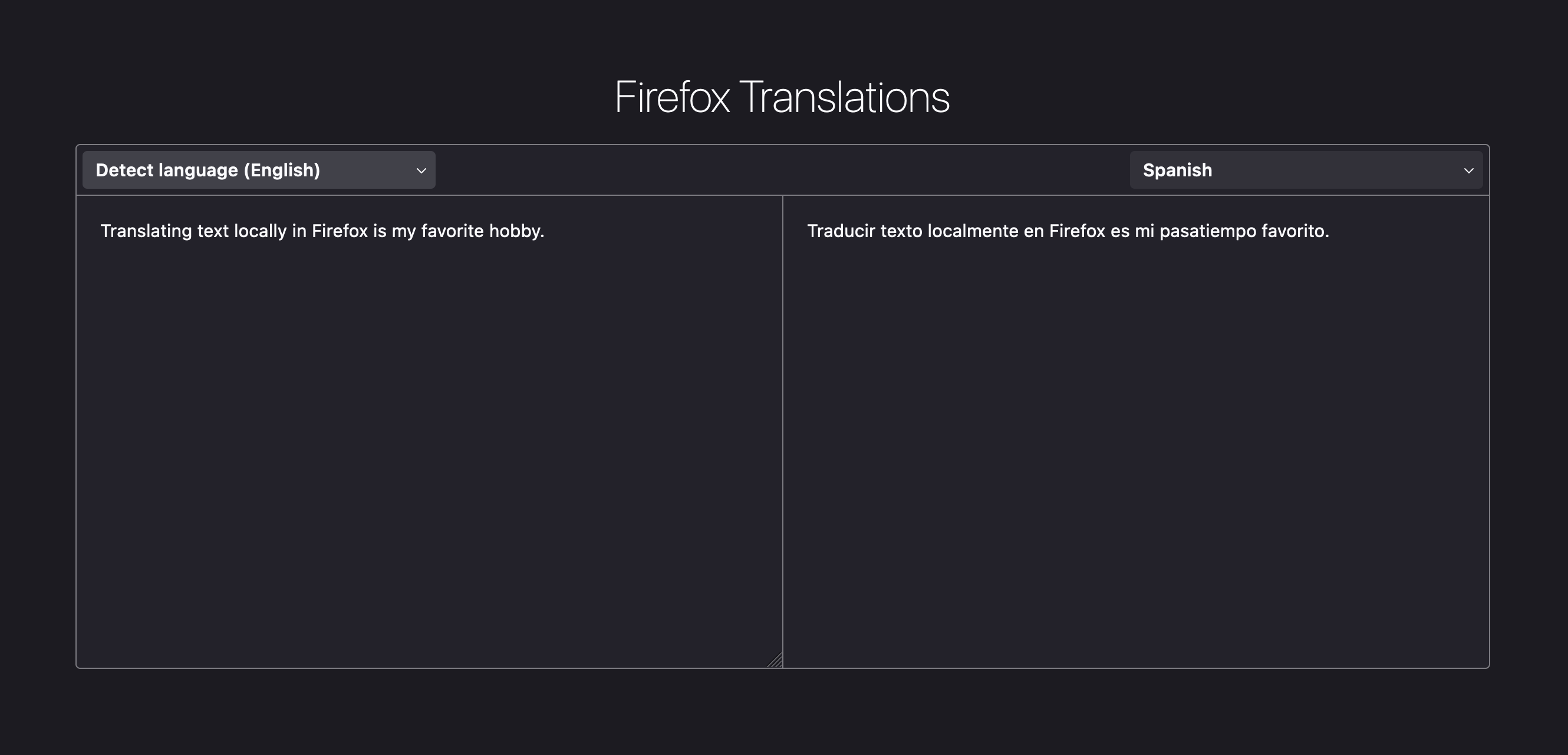
about:translations
about:translations is a test page where there user can select a source language and a target language by typing content into
the source-language text box and seeing the translated text in the target-language text box.
Note
about:translations is a developer-focused UI that is useful for testing the state, performance, and quality of the language models in an interactive environment. It is fairly unpolished and not intended to be shipped as a product at this time.
It is, however, useful and fun, so it is documented here.