Default Search Engines
Default Engine
The search service specifies default search engines via the configuration schema.
Changing Defaults
The default engine may change when:
The user has the default engine set and the configuration for the locale/region changes.
The user has the default engine set and their locale/region changes to one which has a different default.
The user chooses to set a different engine via preferences.
The user installs an add-on which sets its default as one of the application provided engines.
The user installs an add-on which supplies a different engine and the user allows the different engine to be set as default.
The user or Firefox (e.g. via blocklist) causes the default engine to be removed.
Add-ons and Prompting for Default
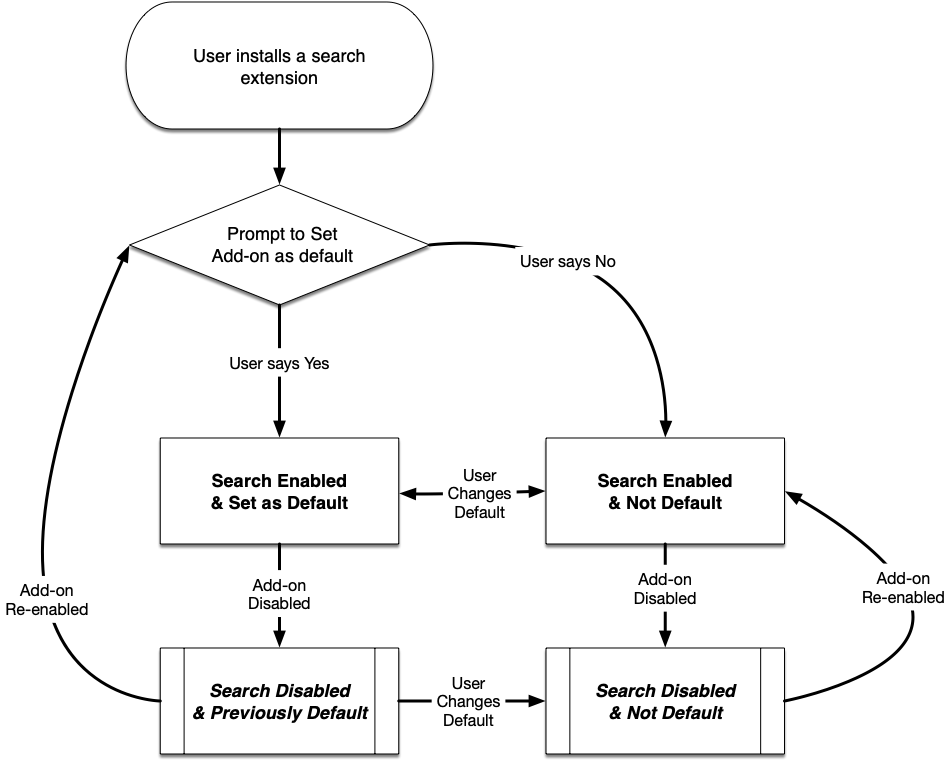
The prompt for selecting a search engine from an add-on as default is shown to the user on installation of the add-on. It may also be shown if an add-on is re-enabled, if the default engine was not changed in the meantime.
The following diagram shows the full flow for search engines from add-ons:
When the Default Engine is Removed
If the default engine is removed by the user, or by Firefox in the case of a blocklist or for some other region, the new default engine is chosen by the following process.
If the default engine specified by the configuration for the user’s region and locale is visible, then it will be selected as default.
If there is another engine visible, fall back to the first engine identified as a general search engine (see below).
If there are no other visible engines, unhide the region/locale default engine from the configuration and set it as default if it is not the one being removed.
Otherwise, unhide the first general search engine, or the first visible engine.
A general search engine is defined as one that returns general search results, for example Google or DuckDuckGo. A non-general search engine returns results for a specific area, e.g. shopping, books, dictionaries.
Add-ons and Config Engines
An add-on may set the name of the search provider in the manifest.json to be the name of a config search engine. In this case:
If the add-on is a non-authorised partner, then we set the user’s default engine to the config engine.
If the add-on is from an authorised partner, then we set the users’ default engine to the config engine, and we allow the config engine’s urls to be overridden with those of the add-on.
If the config engine is already default, then the add-on does not override the config engine, and it’s settings are ignored and no new engine is added.
The list of authorised add-ons is stored in remote settings in the search-default-override-allowlist bucket. The list includes records containing:
Third-party Add-on Id: The identifier of the third party add-on which will override the config one.
Add-on Id to Override: The identifier of the config search engine to be overridden.
a list of the url / params that are authorised to be replaced.
When an authorised add-on overrides the default, we record the add-on’s id
with the config engine in the overriddenBy field. This is used
when the engine is loaded on startup to known that it should load the parameters
from that add-on.
The overriddenBy annotation may be removed when:
The associated authorised add-on is removed, disabled or can no longer be found.
The user changes their default to another engine.
If the overriddenBy annotation is present, but the add-on is not authorised,
then the annotation will be maintained in case the add-on is later re-authorised.
For example, a url is updated, but the update is performed before the allow list
is updated.